I. Formed parts
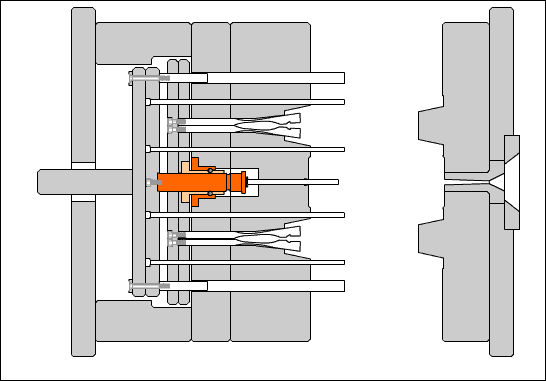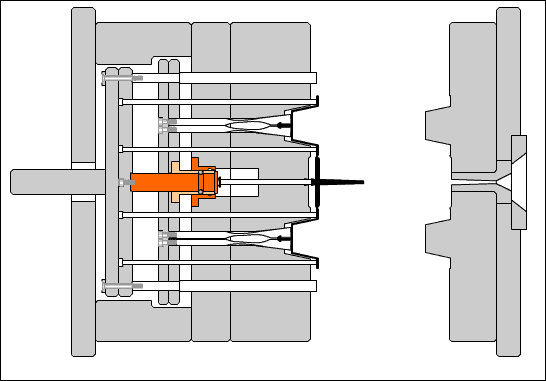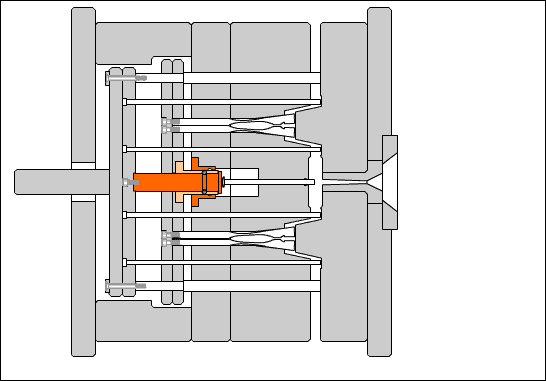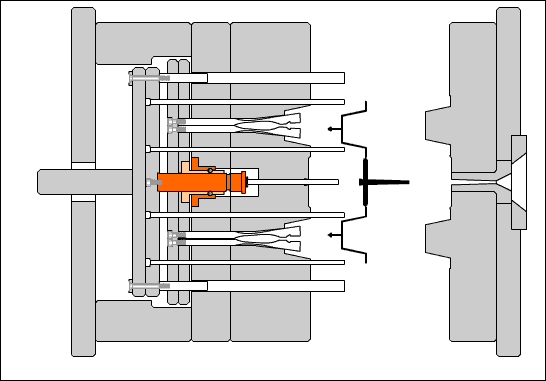
Cavity (mold): The concave part of the surface of the molded plastic part.
Concave template (cavity plate): A plate-like part with a concave profile on the surface of the molded part. It is placed in the fixed mold part and is called the fixed mold cavity plate. It is placed in the movable mold part and is called the movable mold cavity plate.
Core: A convex part on the inner surface of a molded plastic part.
Side core: A core that forms the side holes, undercuts, or side bosses of a molded part, and can be manually or with a slider that performs extraction and reset movements within the mold.
Insert: When the cavity or core has parts that are easily damaged or difficult to process as a whole, it is manufactured separately from the main body and embedded into the partially formed part of the main body.
Activity insert: A shaped part that must be molded with the plastic part to be separated according to process and structural requirements.
Block: Several separately manufactured forming parts used to assemble a die or core, which can be referred to as die blocks or core blocks.
Threaded core: A forming part that forms internal threads in a plastic part, which can be a movable threaded core (removed from the mold) or a threaded core that rotates within the mold.
Threaded ring: a shaped part that forms the external thread of a plastic part, which can be a movable threaded ring (integral or split) or a threaded ring that rotates within the mold.
II. Guide Parts
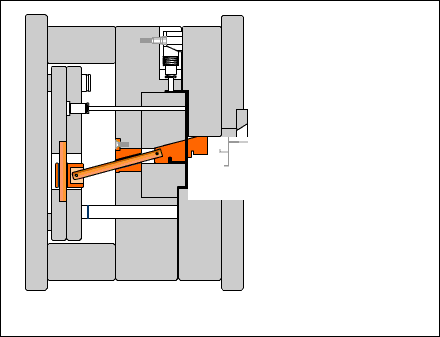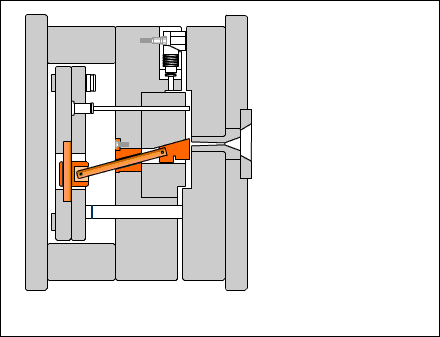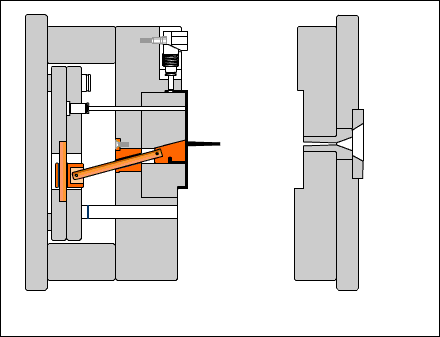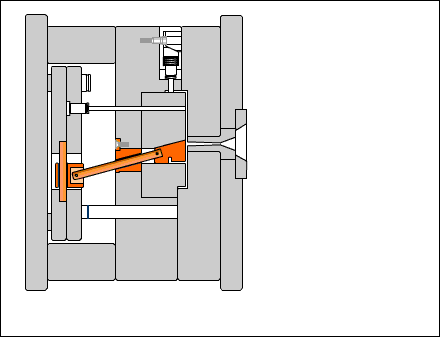
Guide post: A cylindrical part that coordinates with the guide sleeve (or hole) installed on the other half of the mold to ensure the precision of the moving mold opening and closing motion. There are two types of guide posts: with a head and with a shoulder.
Push plate guide pillar: It is a cylindrical pillar that slides with the push plate guide sleeve (or hole) and is used for the motion guidance of the demolding mechanism.
Guide sleeve: A circular sleeve-shaped part that cooperates with the guide post installed on the other half of the mold to ensure the relative position of the moving and stationary molds and the precision of the mold opening and closing motion. There are two types: straight guide sleeve and head guide sleeve.
Push plate guide sleeve: fixed on the push plate, in sliding fit with the push plate guide post, used for guiding the movement of the demolding mechanism.
III. Introducing parts
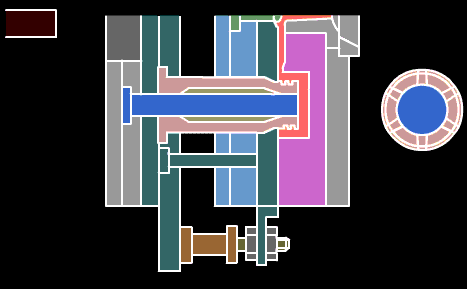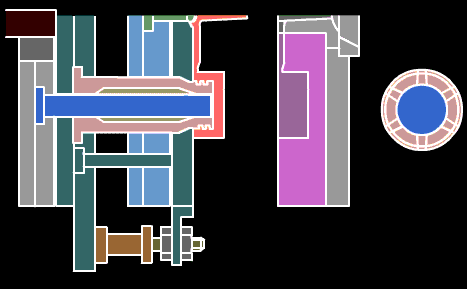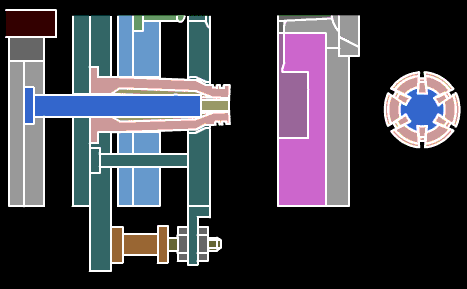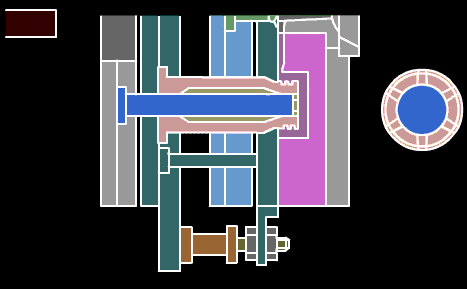
Push rod: A rod that directly pushes out the plastic parts or the condensed material of the injection system. There are cylindrical head push rods, shoulder push rods, and flat head push rods. The cylindrical head push rod can be used to push the top plate, also known as the pre-rod.
Push tube: directly push the tubular part of the plastic part.
Push plate: a plate-shaped part that directly pushes out plastic parts.
Push ring: A ring-shaped or disk-shaped part that partially or entirely pushes out a plastic part.
Push rod fixing plate: a plate-shaped part that fixes the push and reset parts and the push plate guide sleeve.
Push rod: a plate that supports the pushing and resetting parts and directly transfers the pushing force of the machine tool.
Connecting push rod: A rod that connects the push plate and the push plate fixing plate to transmit the pushing force.
Pull rod: It is located directly opposite the main flow channel and has a special head shape that can pull out the condensed material in the main flow channel. The head shape can be Z-shaped, ball-shaped, inverted cone-shaped, mushroom-shaped, conical-shaped, etc.
Pushing channel plate: A plate that pushes the condensed material of the gating system out as the mold opens. Also known as the push plate.
Fourth, core-pulling (parting) parts
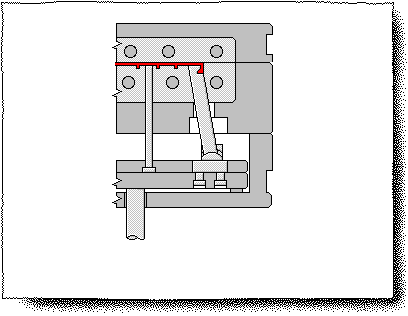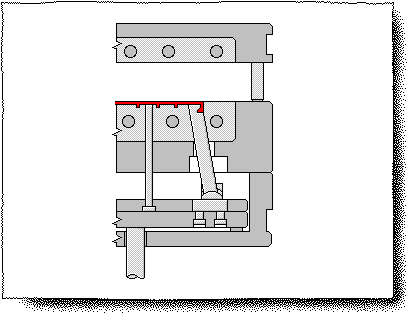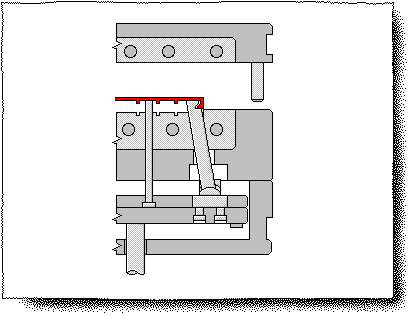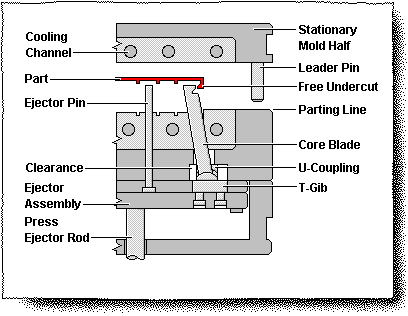
Slant pin (inclined guide pillar): A cylindrical part that is inclined to the parting surface assembly and causes the slider (or die piece) to reciprocate within the mold as the mold opens and closes.
Slide: A part that moves along a guide structure to drive the side core (or die piece) to complete the core pulling and resetting actions.
Side core slider: A side core or slider made of monolithic material. Sometimes several sliders form a mold piece, which needs to be separated before the plastic part can be smoothly ejected.
Slide guide plate: a plate that cooperates with the sliding surface of the slide to guide the sliding.
Wedge block: a part with an oblique angle used to lock the slider during mold closing.
Bending pin: A rectangular or square section bending part that enables the slider to perform core-pulling and resetting movements as the mold opens and closes.
Slanting slider: A concave mold piece that uses the cooperation of a slope and a mold sleeve to produce sliding, with the functions of forming, pushing out, and core pulling (parting).
Slanted guide plate: a plate-shaped part with a slanted guide slot that allows the slider to perform core-pulling and resetting movements as the mold opens and closes.
V. Supporting and fixing parts
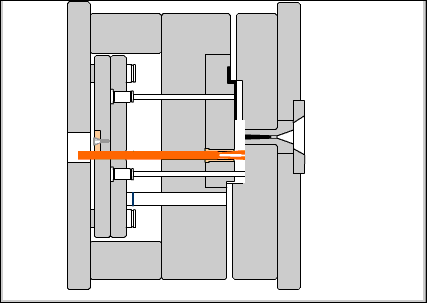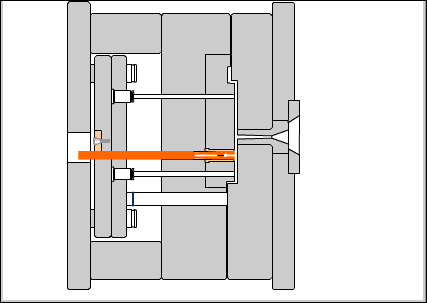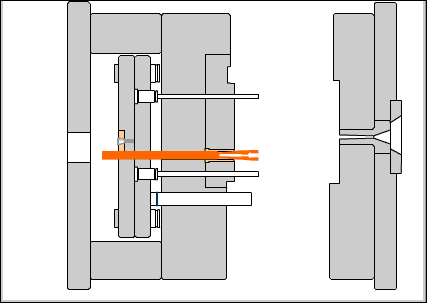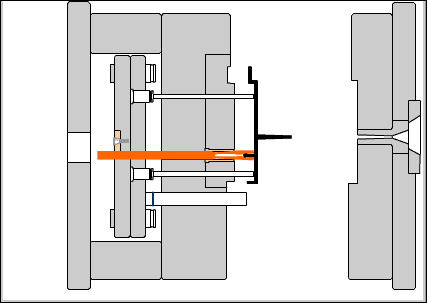
Positioning base plate: a choice to secure the base plate on the fixed workbench of the injection machine.
Moving mold base plate: The plate that holds the moving mold on the moving table of the injection machine.
Die fixing plate: a plate-shaped part that fixes the concave (cavity), also known as the cavity fixing plate.
Core fixing plate: a plate-shaped part that fixes the core.
Mold sleeve: A frame-shaped structural part that positions and fastens inserts or pieces together, or a frame-shaped part that secures a female mold or core.
Support plate: a plate that prevents axial displacement of the forming parts (molds, cores, or inserts) and guide parts, and withstands the forming pressure.
Pad: A block-shaped part that adjusts the height of the mold closure to form the pushing space required for the demolding mechanism.
Support: It adjusts the mold closing height, forms the required ejection stroke space for the demolding mechanism, and enables the moving mold to be fixed on the “L” shaped block part of the injection machine, also known as the mold foot.
Support column: A cylindrical part that is placed between the dynamic mold support plate and the dynamic mold base plate to enhance the rigidity of the dynamic mold support plate and provide support.
VI. Positioning and Limiting Parts
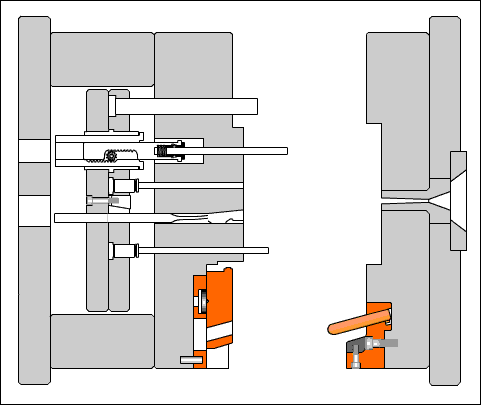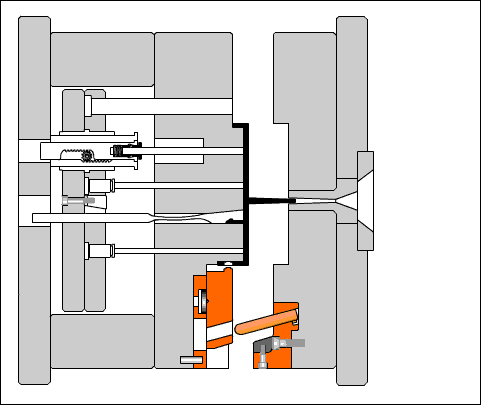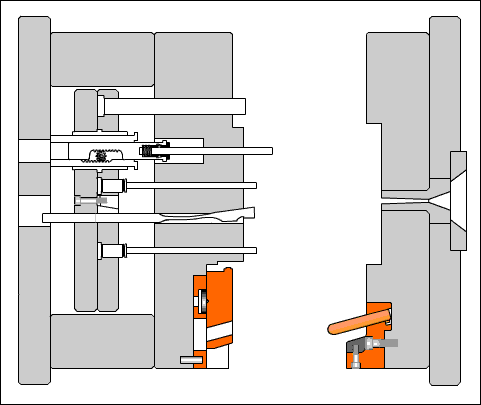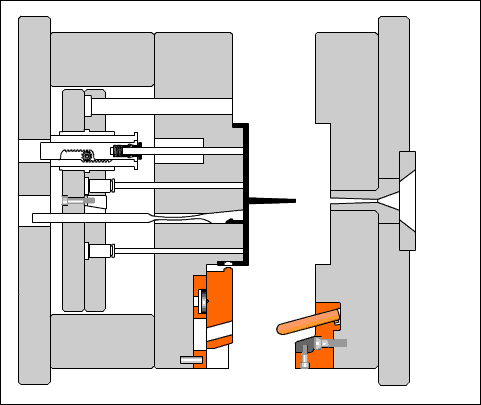
Positioning ring: A circular or circular plate-shaped part that aligns the mold main runner with the injection machine nozzle and determines the installation position of the mold on the injection machine.
Conical locating piece: When closing the mold, use the corresponding conical surface to accurately position the moving and stationary mold parts.
Reset rod: A rod fixed to the push rod fixing plate that restores the demolding mechanism through the closing action of the mold.
Limit pin: It plays a supporting and adjusting role for the demolding mechanism, and prevents the demolding mechanism from being obstructed by foreign objects during resetting, or limits the final position of the rod after the slider core-pulling.
Fixed distance pull rod: a rod used to limit a template to pull or stop within a limited distance during mold opening and parting.
Positioning pin: A cylindrical rod that fixes the position of two or more templates relative to each other to prevent displacement.
Fixed distance pulling plate: a plate used to limit a certain template to pull or stop within a limited distance during mold opening and parting.
VII. Cooling and heating parts
Cooling water nozzle: a pipe fitting used to connect rubber hoses and supply cold water into the mold.
Baffle: A metal strip or plate placed in the cooling water channel of the mold to change the direction of the cooling water flow
Heating plate: A plate with heating structure, such as hot water (oil), steam, or electric heating elements, is set up to ensure that the mold temperature meets the requirements of the plastic forming process.
Heat shield: a plate that prevents the transmission and diffusion of heat.
VIII. Others
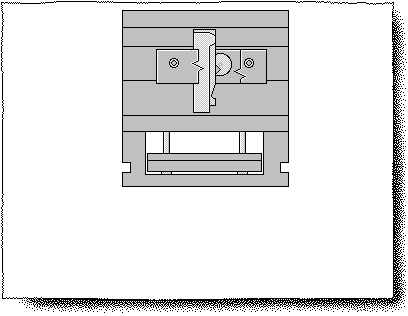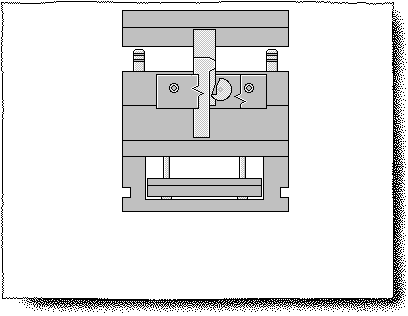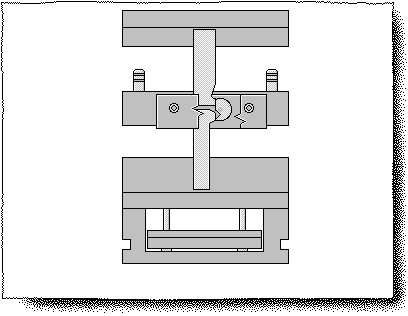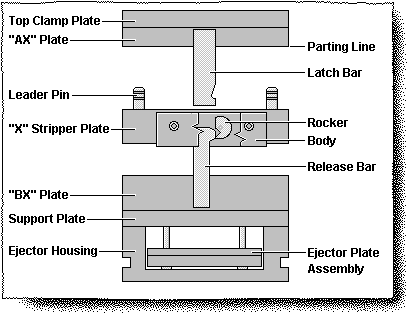
Gate: A bushing part with a main runner channel that directly contacts the nozzle of the injection machine.
Gate insert: To improve the service life of the gate, replaceable wear-resistant metal inserts are used for the gate.
Flow channel plate: a plate specially designed for the opening of the diversion channel, which can be divided into hot flow channel plate and warm flow channel plate.
Secondary nozzle: A nozzle that provides a direct or indirect feed channel from the hot runner plate (column) to the mold cavity.
