Molding and processing methods used for plastic household appliances generally include injection molding, extrusion molding, thermal molding, hollow molding, laminated molding compression molding transfer molding foam molding pouring molding inlay casting sealing casting etc. Of these processes injection molding stands as the predominant one.

Recently, several cutting-edge plastic manufacturing technologies and equipment have become widespread tools in molding plastic products for household appliances, such as precision injection molding, rapid prototyping technology, melt core injection molding technology, gas assisted/water assisted injection molding technology, electromagnetic dynamic injection molding technology and film-coated injection molding technology.
1. Accuracy injection molding
With injection molding technology, high accuracy and repeatability in terms of size and weight of products can be ensured, along with high pressure/speed injection capability for injection molding machines using this technique. Furthermore, due to open or closed loop control mechanisms in injection process parameters used by such injection molding machines utilizing this technology.
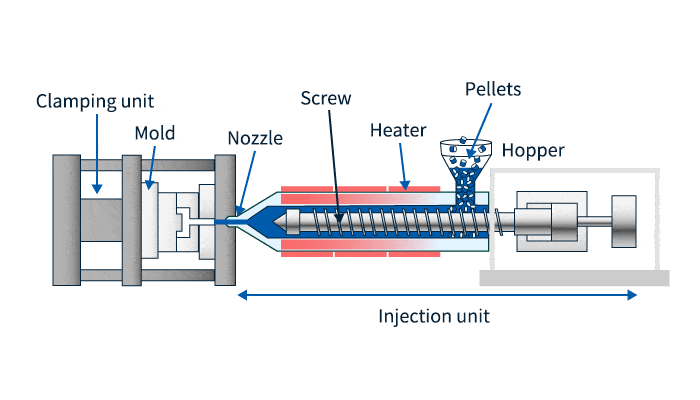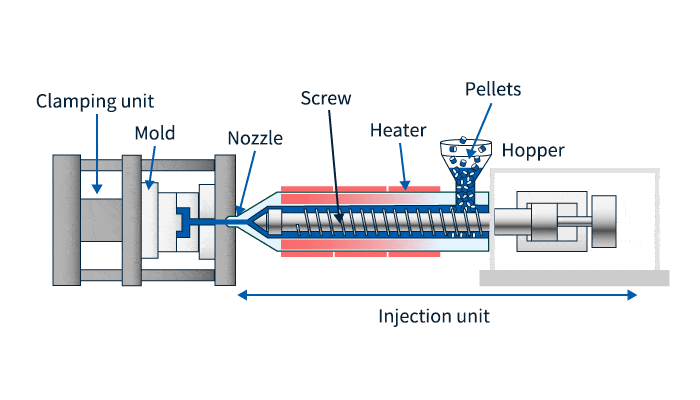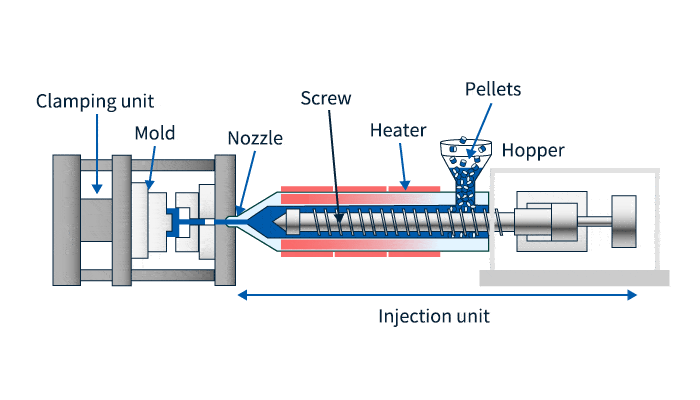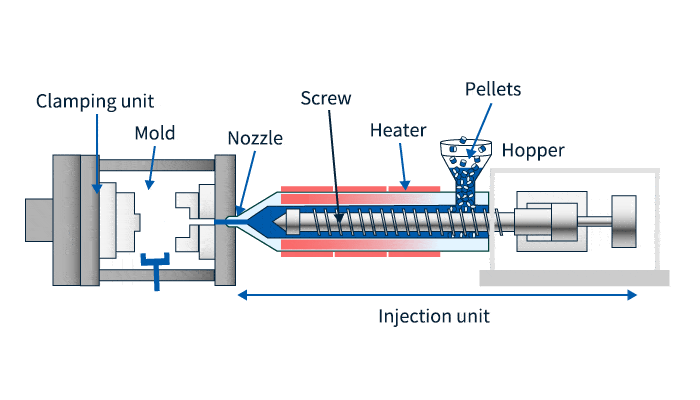
Precision injection molding requires highly precise molds; China currently manufactures small and medium-sized precision injection molding machines suitable for this task.
2. Rapid prototyping technology
Home appliance manufacturing technology has experienced explosive growth along with their diversification and upgrade; most commonly this technique is employed for creating plastic housings for home devices, and boasting small scale production without molds being required for production of such items.
At present, laser scanning and liquid light curing are two effective rapid prototyping methods, of which laser scanning is one of the more mature rapid prototyping processes available. Laser scanning equipment consists of a laser light source, scanning device, powder spreading device and computer for processing; when scanning along a specific trajectory controlled by computer the laser head heats and melts plastic powder at certain spots along its path; after each scan using powder spreading device thin layer is spread so as to create product with specific shape/size after repeated tracings.
At present, certain domestic enterprises produce laser scanning molding machines and plastic micro powder, but its performance remains unpredictable while its range and grades remain limited.
3. Molten Core Injection Molding Technology
Hollow molding or rotational molding methods cannot provide enough precision or roughness for these irregular cavity products, thus forcing this form of manufacturing on them. This molding technique should only be utilized if there are special circumstances whereby hollow or rotational methods cannot be processed properly.
Presently, this technology is relatively advanced in foreign countries but remains at an early stage in China. To utilize it properly, its processing principle involves first creating the core shape which forms the cavity before employing that core as an insert injection molding mold.
Under the heating effect of injection molded parts, core type material melts and flows out, creating cavities. One key aspect to using this technology successfully is mastering its melting point relationship between core material and plastic part – in general terms this should include selecting general-use plastics such as general purpose polystyrene plastics or thermoplastic elastomers or low melting metals such as lead or tin for use as core type materials.
4. Gas/water assisted injection molding
Injection molding is widely utilized for producing various injection molded parts, including television enclosures. Gas or superheated water may be introduced directly into the mold cavity almost simultaneously with plastic melting, providing immediate mold fill.
At this stage, plastic melt will be coated with gas or superheated water to form sandwich structures for plastic products being formed through molding equipment. Once set in their molds, excess gas or water may be discharged to release them – creating products with material savings, low shrinkage rates, aesthetic appeal, and excellent rigidity that have numerous advantages for customers. A gas or water assisted device along with its control software constitute the core part of molding equipment used during molding operations.
Recently in China there has been extensive research conducted and applications are accelerated rapidly; however, domestic equipment remains uncertain and unreliable.
5. Electromagnetic dynamic injection molding technology
This technology involves making use of electromagnetic force to cause the screw to vibrate reciprocally in its axial direction, with vibration being generated via electromagnetic vibrations. Due to microscopic plasticization during pre-plasticization stage, packing stage structures become more compacted while internal stress decreases dramatically for products produced.

This technology can be utilized for molding products with stringent requirements, such as optical discs. When used to mold ordinary products, its quality-improvement properties may even further strengthen them.
6. Film-coated injection molding technology
Utilizing this technology requires inserting a special printed decorative plastic film into a mold prior to injection molding, whereupon its heat deformation allows it to stick securely onto the surface of a plastic part without further decoration steps afterward. Not only can this reduce post-decoration steps while simultaneously looking beautiful and durable.
Under usual conditions, household appliance makers typically need an abundance of plastic molds for household appliances like fridges or washing machines requiring fully automatic functionality require over 100 molds; an air conditioner requires 20+, while color TV sets need 50-70 plastic molds each for manufacture.
At the same time, technical requirements for plastic molds are quite stringent and frequently necessitate a short mold processing cycle to facilitate mold design and modern manufacturing technologies. Furthermore, more challenging mold types such as hot runner injection molds and laminated injection molds have found domestic applications over time.
