What Is Injection Molding
Injection molding is a combination of injection and molding processes. Its advantages include fast production speeds, high efficiency operations, automated operation systems and wide patterns that range from complex to simple shapes; sizes that can be reduced from large to small; accurate product sizes that are easy to update or replace as well as producing complex shaped products – perfect for large-scale production environments or processing. Injection molding methods make use of injections in manufacturing.
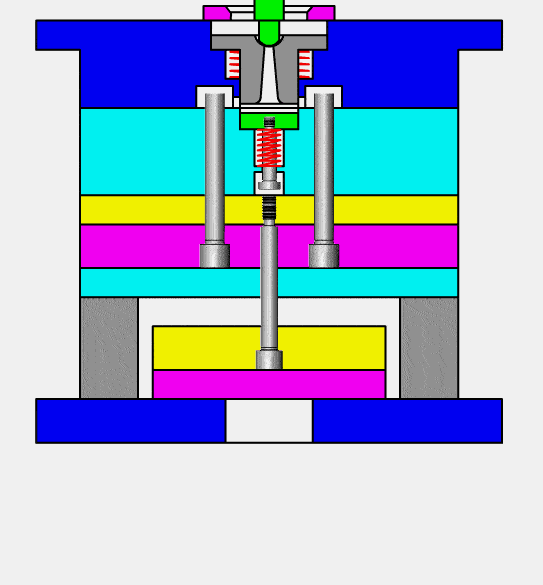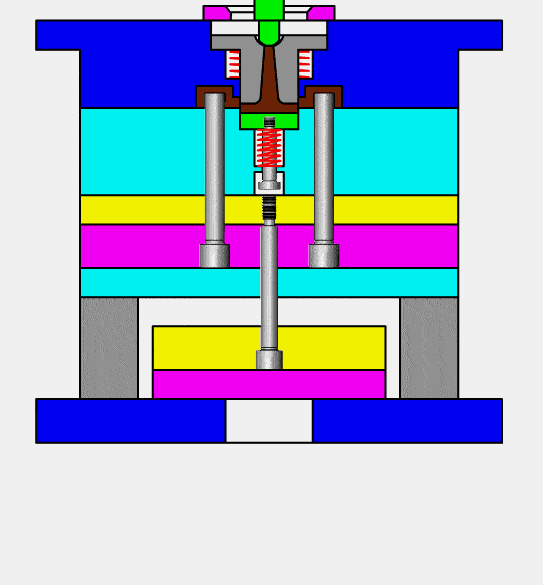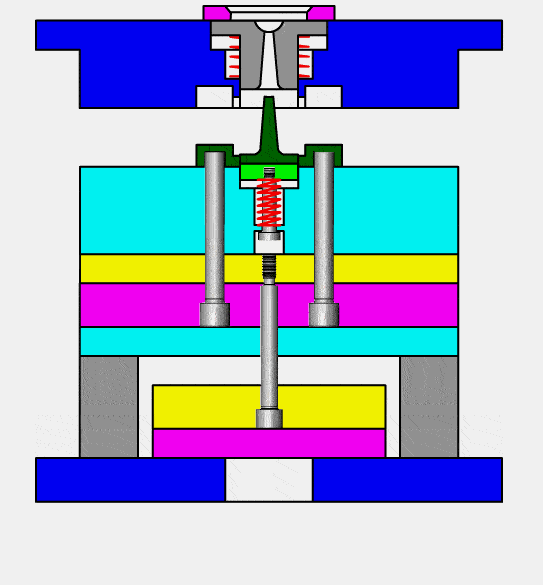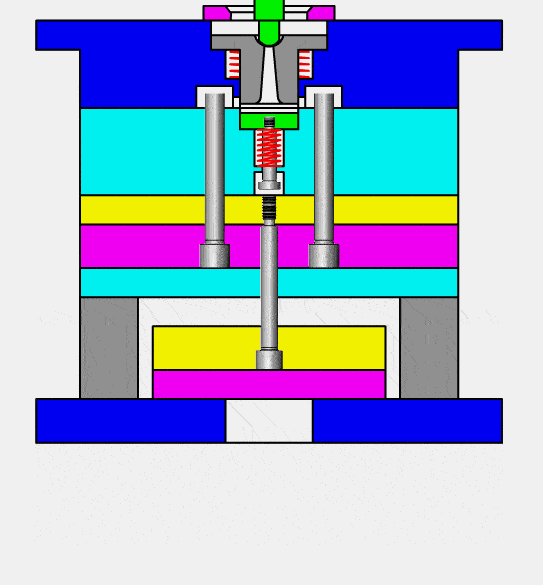
injection molding (or thermoplastic molding) is the process of producing molded products by stirring fully melted plastic material with a screw at a certain temperature, injecting it under high pressure into a mold cavity at this same temperature and cooling and solidifying it afterwards. It is an efficient means for mass producing complex shaped components and is one of the primary processing techniques available today.
The injection molding process can generally be divided into six stages: Mold closing, injection molding, pressure holding, cooling (feeding), mold opening and ejection (product removal).
Introduction to Injection Molding Principles
This injection molding process can be repeated again and again for mass production of products in batches and on a continuous basis. Molding thermosetting plastics and rubber follows the same general process; however, the temperature in the material barrel tends to be lower and injection pressure higher; heating of the mold prior to material injection must occur as well as subsequent curing/vulcanization and then demolding processes before demolding takes place while still hot.
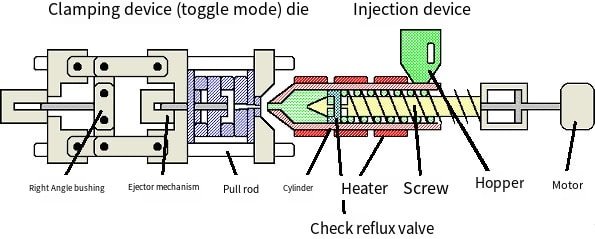
Injection molds contain seven main systems: pouring system, guiding system, forming system, core pulling system, ejection system, cooling system and exhaust system.
1.Pouring System: main flow channel, diversion channel, gate and cold material well.
2.Guidance System (Guidance Pillars, Guide Sleeves and Positioning Blocks, among other components).
3.Forming System (Mold Core, Inlay Block etc).
4.For Core Pulling system (4 Core Pulling systems (slider diagonal pin etc), etc).
5.Ejection system with Ejector Pin/Ejector Block.
6.Cooling system: Heat dissipation from the mold itself and water cooling.
7.Exhaust system: Fitting clearance between each insert in the mold and an ejector pin as well as any additional exhaust grooves are important considerations in exhaust systems.
